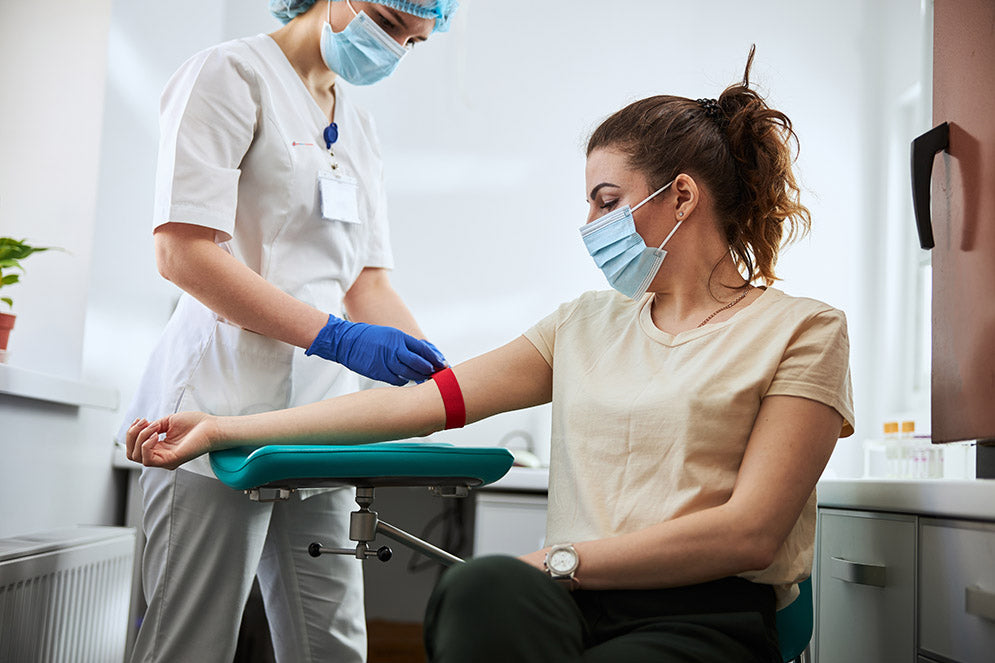
About the Vitamin D (25-OH) Blood Test
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes in the human body. Vitamin D is produced in the skin when it is exposed to sunlight and manifests itself in the more biologically active form of D3.
Apart from being essential for healthy bones, hair and skin, adequate vitamin D levels are associated with a lower risk of heart disease. It may help regulate blood pressure and reduce inflammation.
Vitamin D is important for muscle strength and function, and deficiency can lead to muscle weakness and pain. Finally, it is important in managing autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and type 1 diabetes - these have all been linked to low vitamin D levels.
Vitamin D can be obtained through dietary sources such as fatty fish (e.g., salmon and mackerel), fortified foods (e.g., fortified milk and cereals), and supplements. However, the body can also produce vitamin D when the skin is exposed to sunlight. Therefore, a balance between sun exposure, diet, and supplements can help ensure sufficient vitamin D levels in the body.